Search Results
Results for: 'Sodium ion'
By: HWC, Views: 5458
The slight positive charge of a hydrogen atom in a water molecule can attract an atom with a slight negative charge, such as the nitrogen in a molecule of ammonia. This forms a hydrogen bond between the two atoms. Hydrogen bonds join the two strands of a DNA molecule. Although hydrogen bo...
By: HWC, Views: 7180
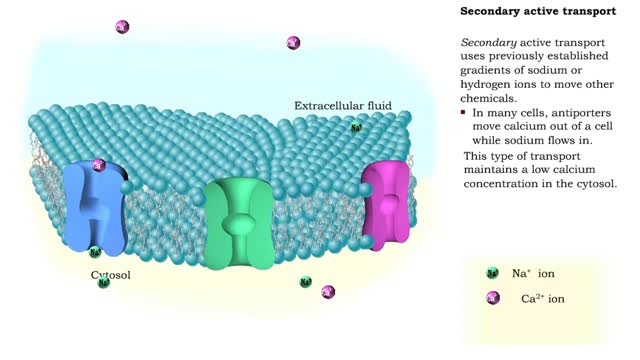
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 6873
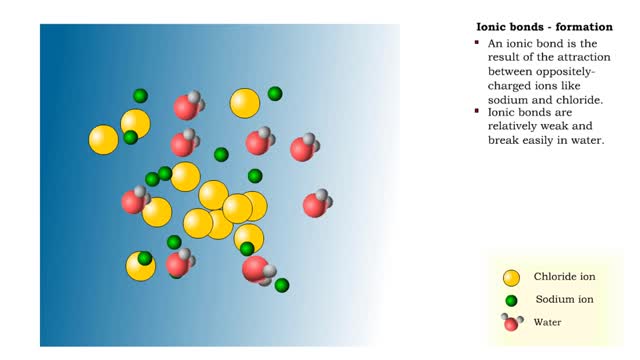
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 7039
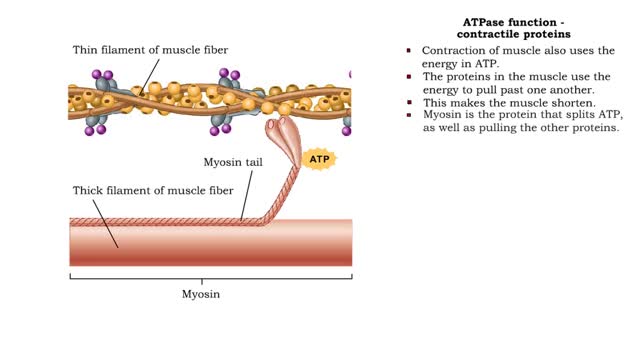
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 3982
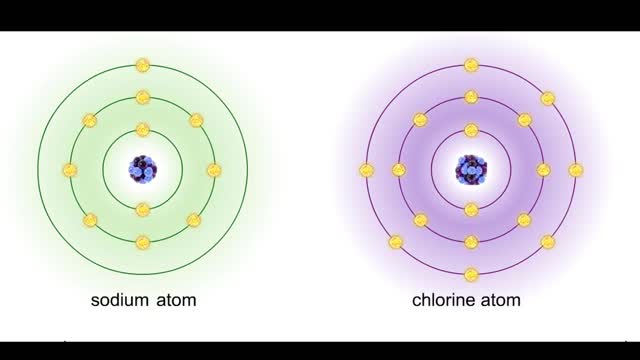
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
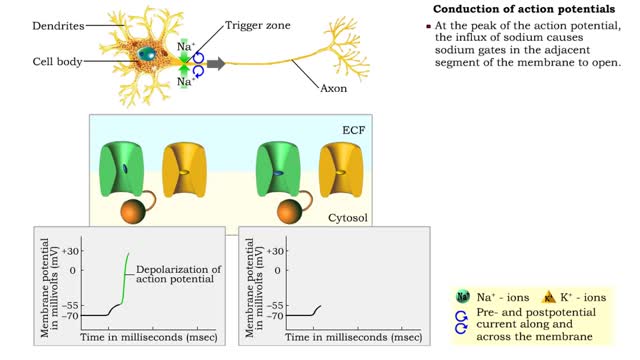
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 6769
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 6251
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
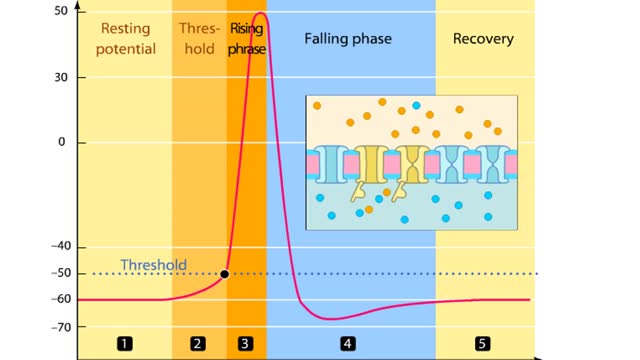
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 6091
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
Advertisement